pacman::p_load(ggdist, ggridges, ggthemes,
colorspace, tidyverse, ggstatsplot,
tidyverse, plotly, crosstalk, DT,
ggdist, gganimate, FunnelPlotR, knitr)Hands-on_Ex04
Getting Start
Installing and loading the packages
Importing data
exam <- read_csv("data04/Exam_data_03.csv")
covid19 <- read_csv("data04/COVID-19_DKI_Jakarta.csv") %>%
mutate_if(is.character, as.factor)Visualising Distribution
Visualising Distribution with Ridgeline Plot
Plotting ridgeline graph: ggridges method
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = ENGLISH,
y = CLASS)) +
geom_density_ridges(
scale = 3,
rel_min_height = 0.01,
bandwidth = 3.4,
fill = lighten("#7097BB", .3),
color = "white"
) +
scale_x_continuous(
name = "English grades",
expand = c(0, 0)
) +
scale_y_discrete(name = NULL, expand = expansion(add = c(0.2, 2.6))) +
theme_ridges()
Varying fill colors along the x axis
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = ENGLISH,
y = CLASS,
fill = stat(x))) +
geom_density_ridges_gradient(
scale = 3,
rel_min_height = 0.01) +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "Temp. [F]",
option = "C") +
scale_x_continuous(
name = "English grades",
expand = c(0, 0)
) +
scale_y_discrete(name = NULL, expand = expansion(add = c(0.2, 2.6))) +
theme_ridges()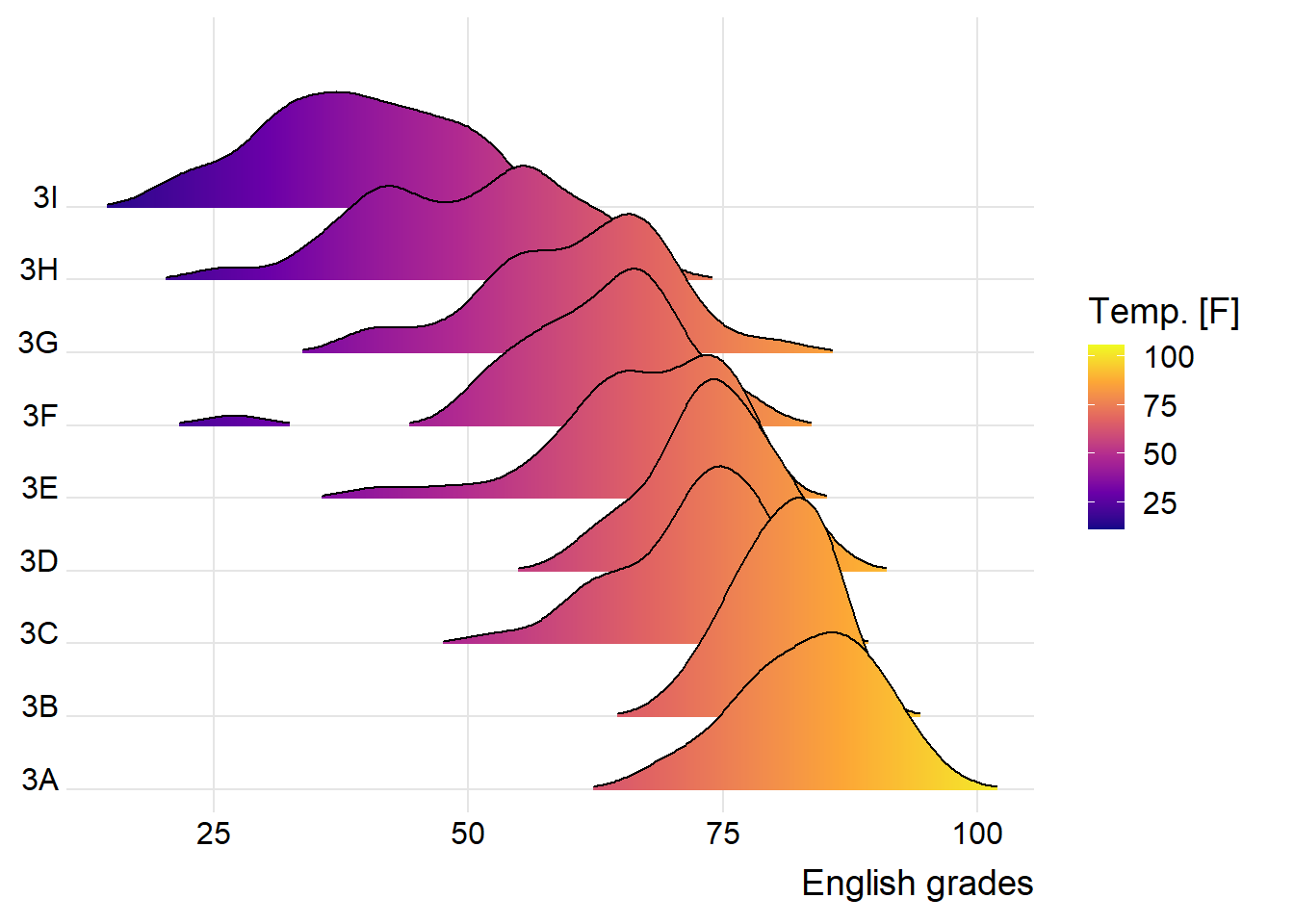
Mapping the probabilities directly onto colour
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = ENGLISH,
y = CLASS,
fill = 0.5 - abs(0.5-stat(ecdf)))) +
stat_density_ridges(geom = "density_ridges_gradient",
calc_ecdf = TRUE) +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "Tail probability",
direction = -1) +
theme_ridges()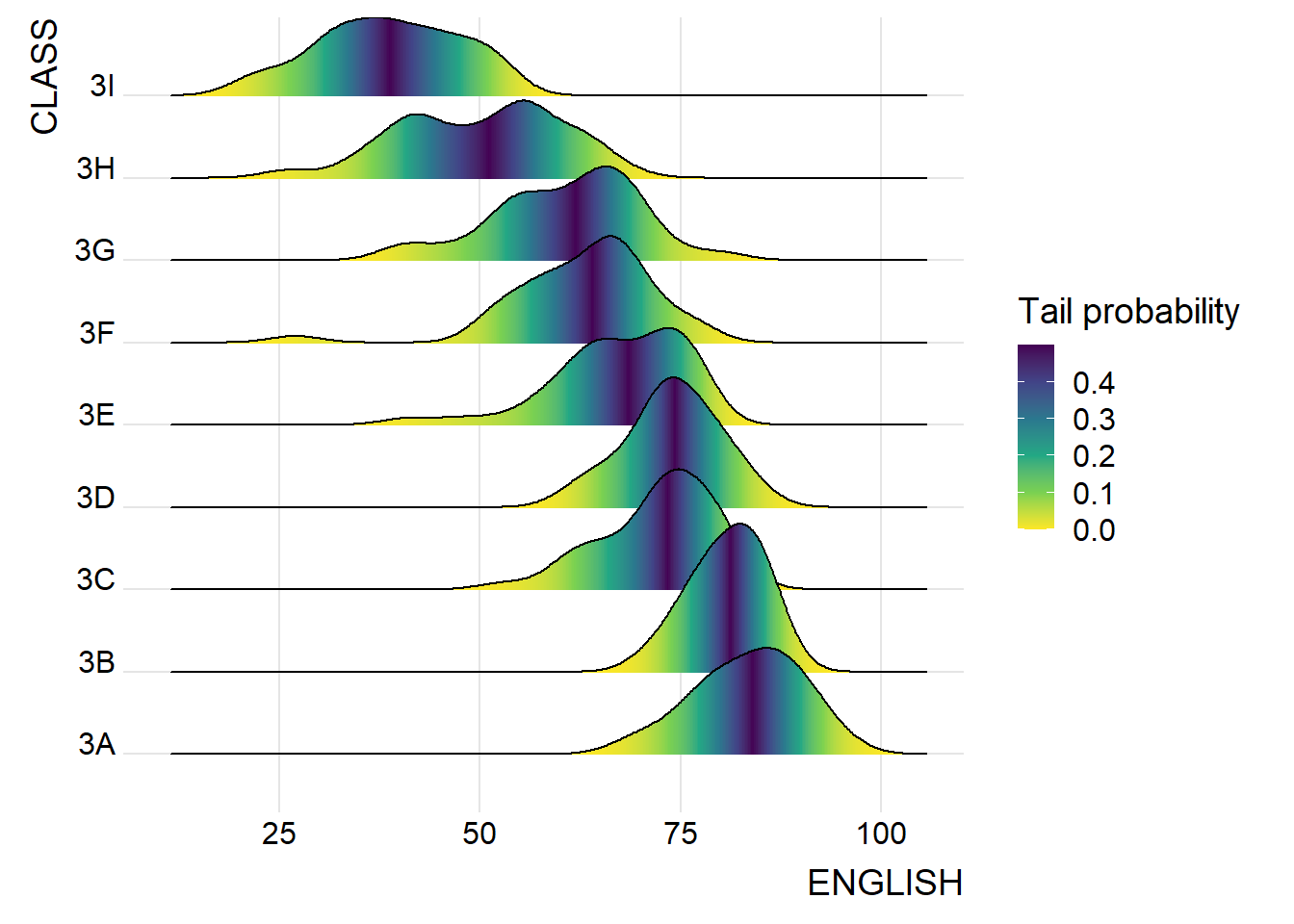
Ridgeline plots with quantile lines
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = ENGLISH,
y = CLASS,
fill = factor(stat(quantile))
)) +
stat_density_ridges(
geom = "density_ridges_gradient",
calc_ecdf = TRUE,
quantiles = 4,
quantile_lines = TRUE) +
scale_fill_viridis_d(name = "Quartiles") +
theme_ridges()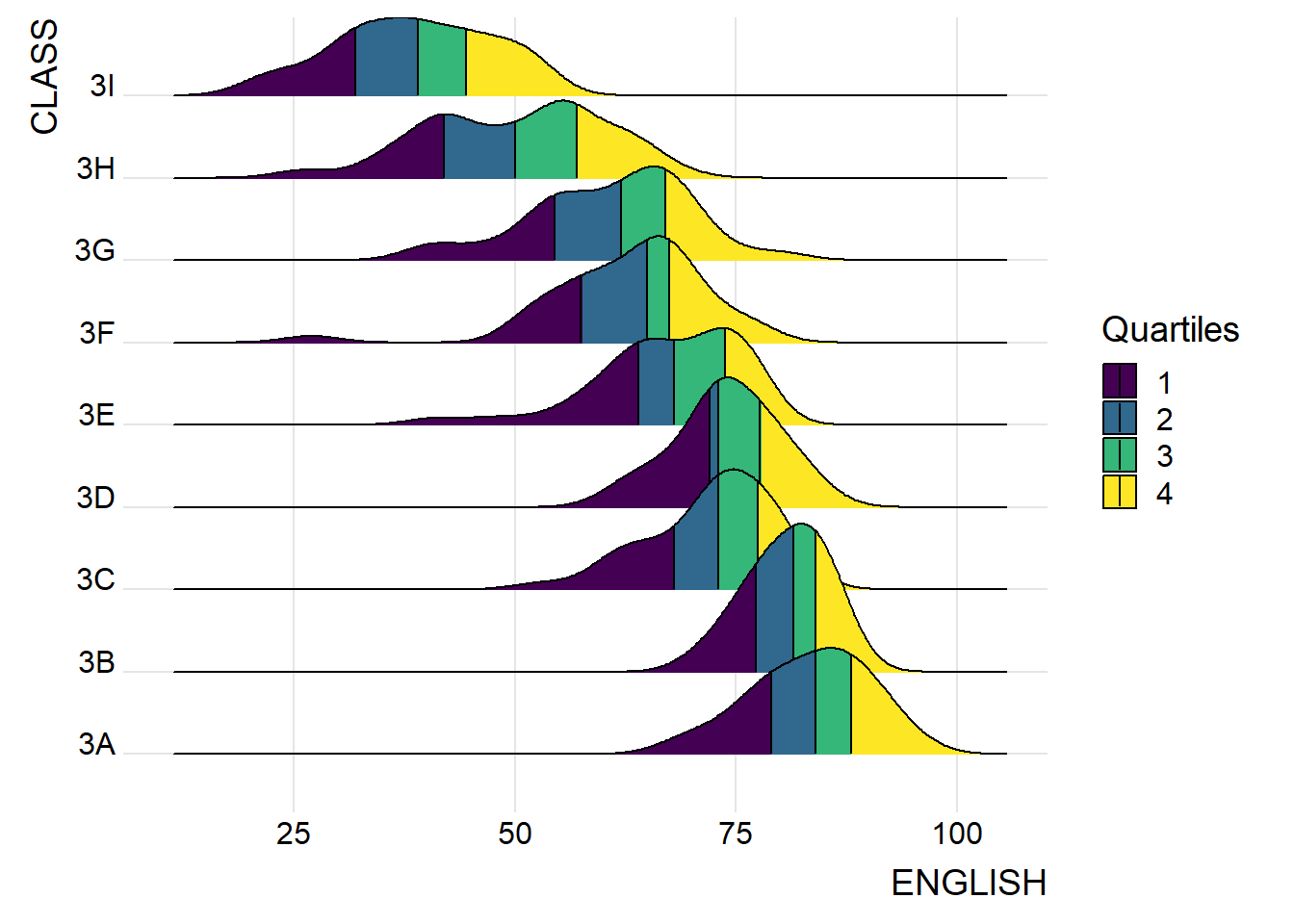
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = ENGLISH,
y = CLASS,
fill = factor(stat(quantile))
)) +
stat_density_ridges(
geom = "density_ridges_gradient",
calc_ecdf = TRUE,
quantiles = c(0.025, 0.975)
) +
scale_fill_manual(
name = "Probability",
values = c("#FF0000A0", "#A0A0A0A0", "#0000FFA0"),
labels = c("(0, 0.025]", "(0.025, 0.975]", "(0.975, 1]")
) +
theme_ridges()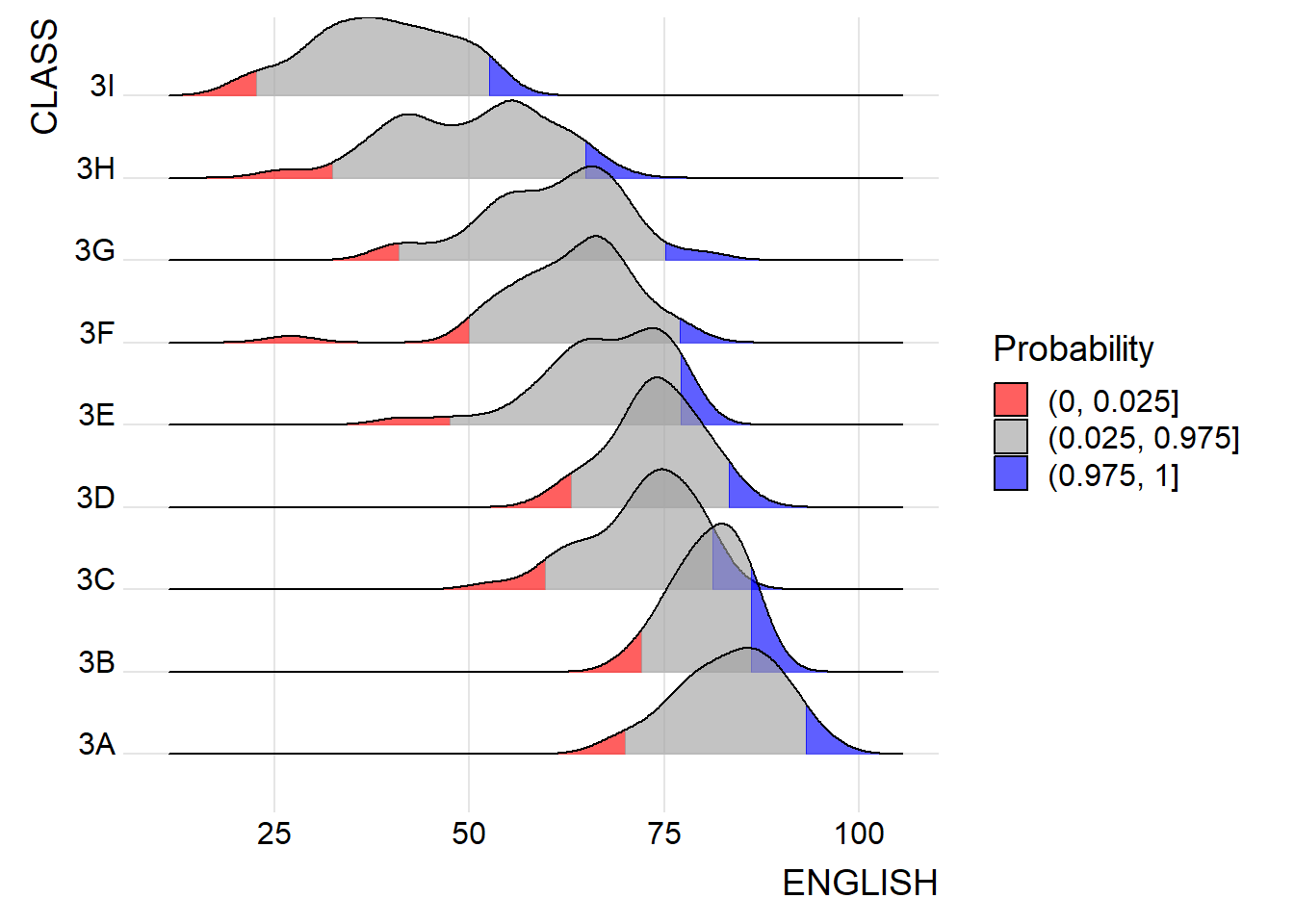
Visualising Distribution with Raincloud Plot
Plotting a Half Eye graph
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = RACE,
y = ENGLISH)) +
stat_halfeye(adjust = 0.5,
justification = -0.2,
.width = 0,
point_colour = NA)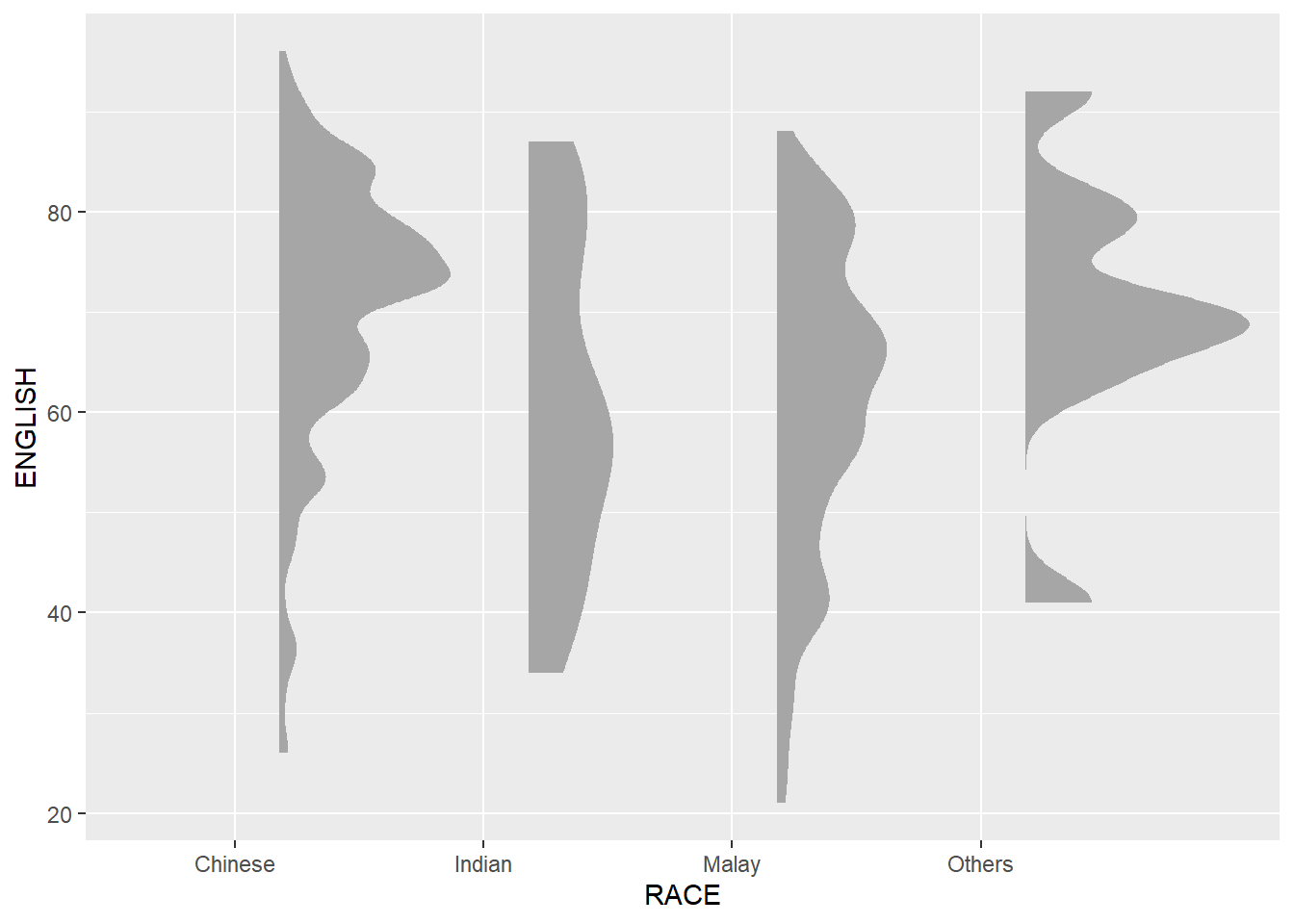
Adding the boxplot with geom_boxplot()
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = RACE,
y = ENGLISH)) +
stat_halfeye(adjust = 0.5,
justification = -0.2,
.width = 0,
point_colour = NA) +
geom_boxplot(width = .20,
outlier.shape = NA)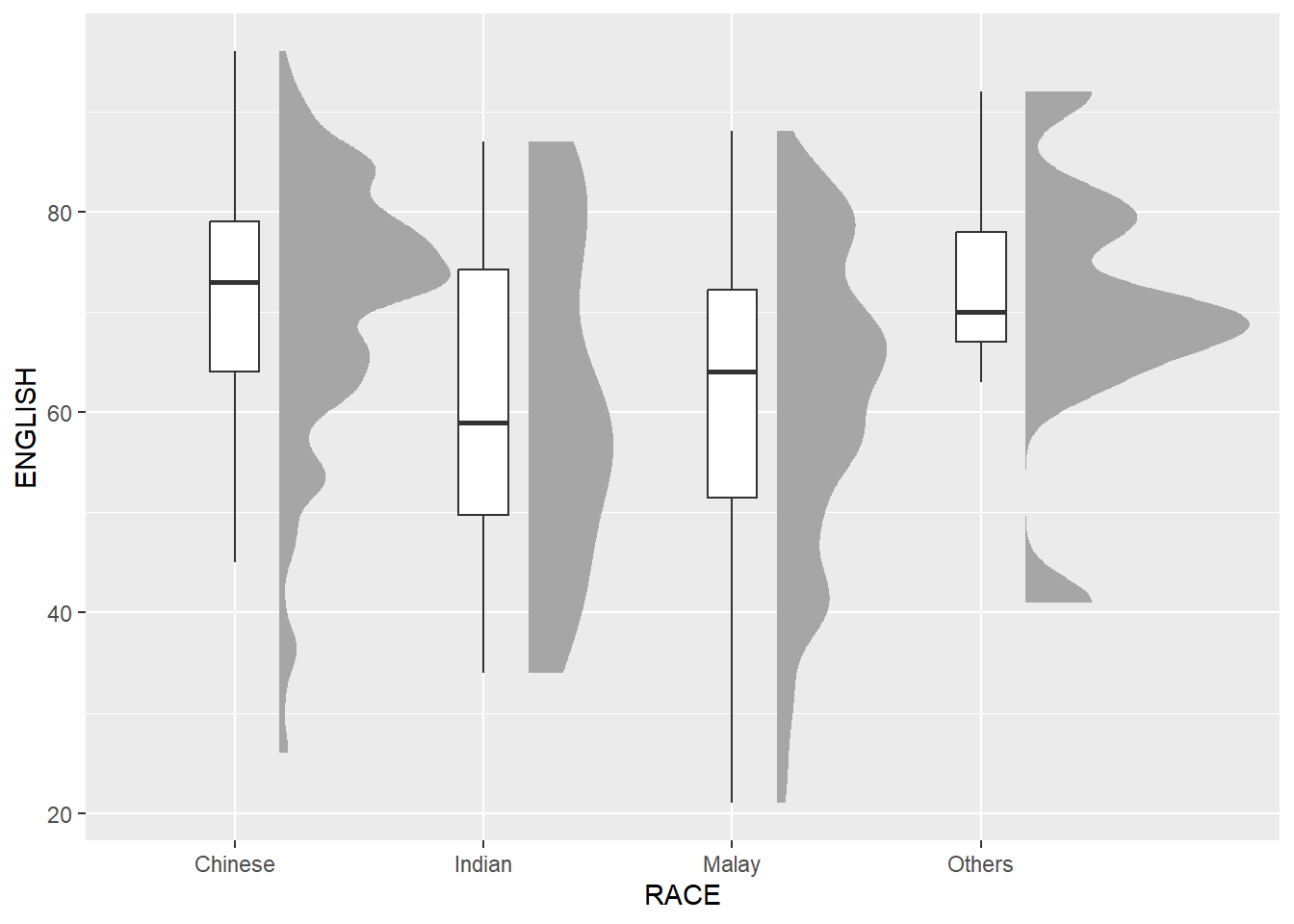
Adding the Dot Plots with stat_dots()
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = RACE,
y = ENGLISH)) +
stat_halfeye(adjust = 0.5,
justification = -0.2,
.width = 0,
point_colour = NA) +
geom_boxplot(width = .20,
outlier.shape = NA) +
stat_dots(side = "left",
justification = 1.2,
binwidth = .5,
dotsize = 2)
Finishing touch
ggplot(exam,
aes(x = RACE,
y = ENGLISH)) +
stat_halfeye(adjust = 0.5,
justification = -0.2,
.width = 0,
point_colour = NA) +
geom_boxplot(width = .20,
outlier.shape = NA) +
stat_dots(side = "left",
justification = 1.2,
binwidth = .5,
dotsize = 1.5) +
coord_flip() +
theme_economist()
Visual Statistical Analysis
Statistical Tests
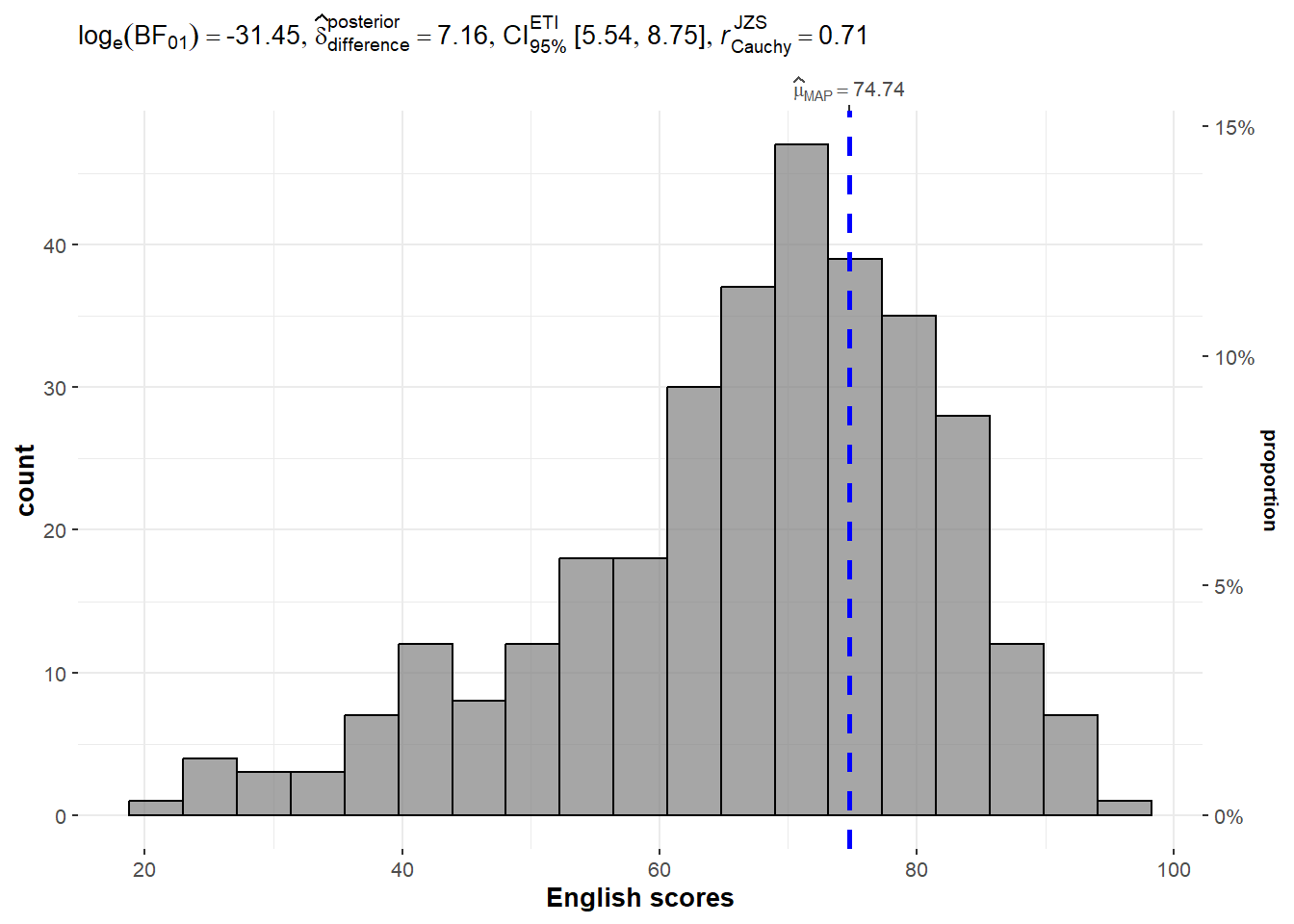
One-sample test: gghistostats() method
set.seed(1234)
gghistostats(
data = exam,
x = ENGLISH,
type = "bayes",
test.value = 60,
xlab = "English scores"
)
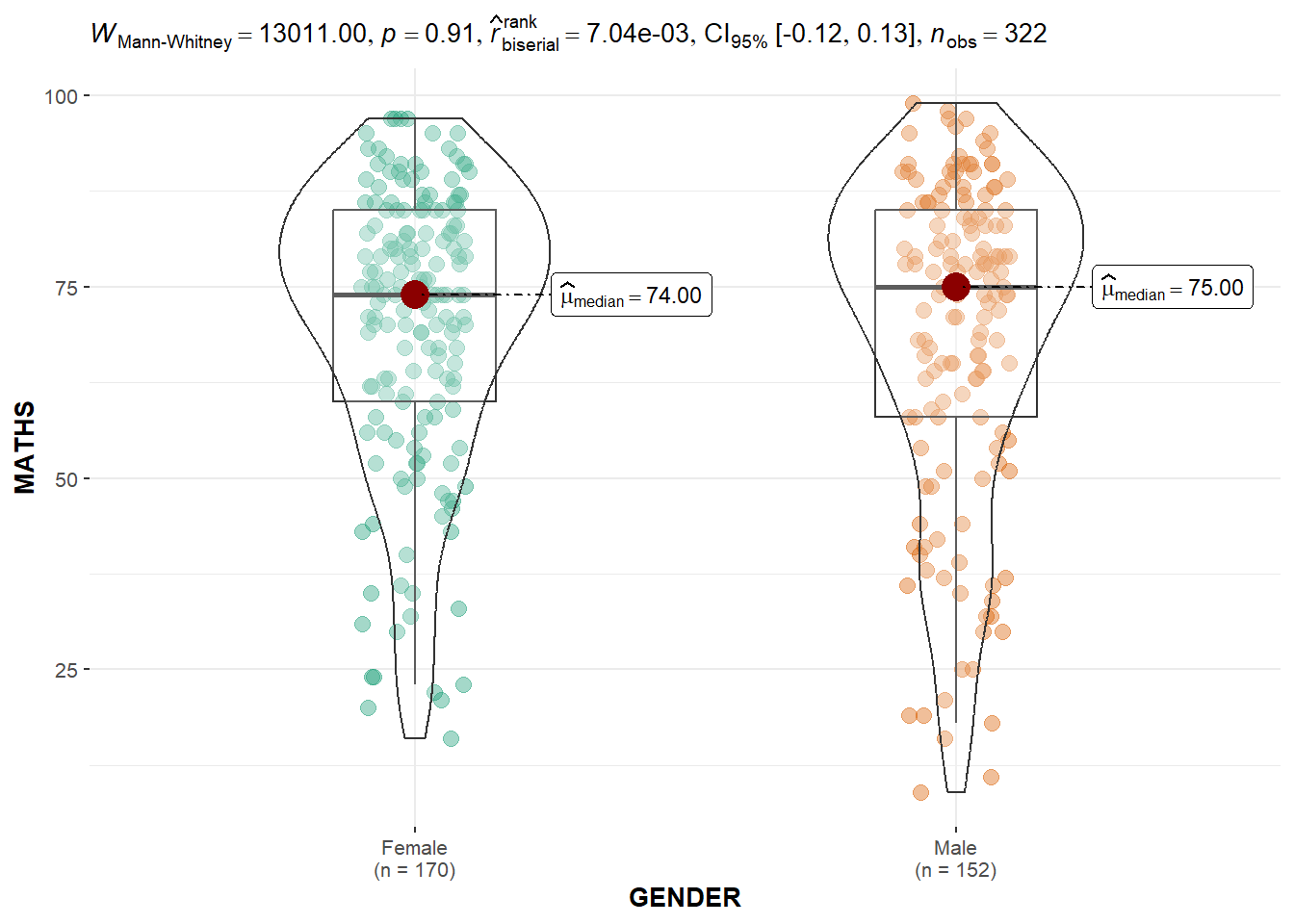
Two-sample mean test: ggbetweenstats()
ggbetweenstats(
data = exam,
x = GENDER,
y = MATHS,
type = "np",
messages = FALSE
)
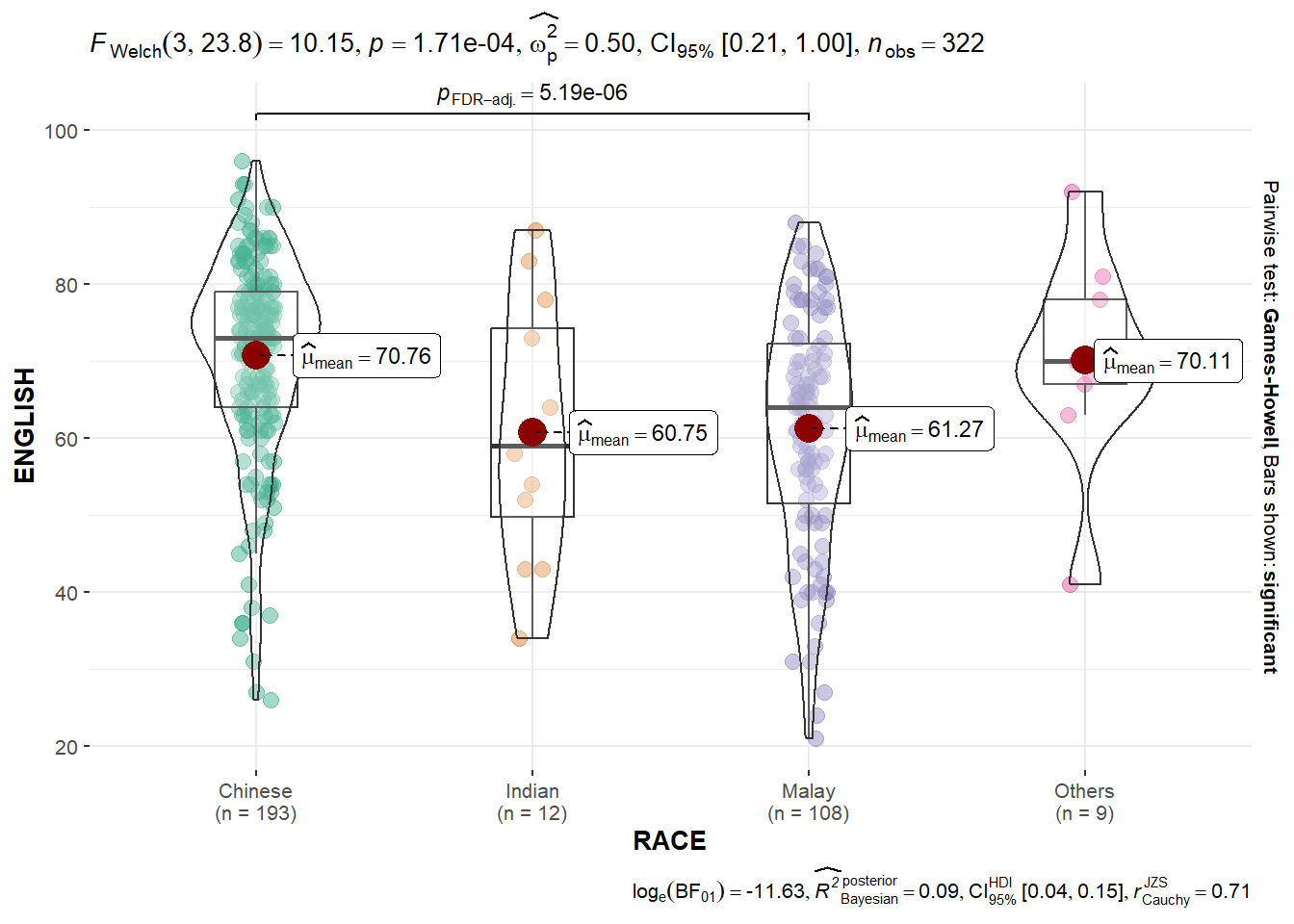
Oneway ANOVA Test: ggbetweenstats() method
ggbetweenstats(
data = exam,
x = RACE,
y = ENGLISH,
type = "p",
mean.ci = TRUE,
pairwise.comparisons = TRUE,
pairwise.display = "s",
p.adjust.method = "fdr",
messages = FALSE
)
Significant Test of Association (Depedence) : ggbarstats() methods
exam1 <- exam %>%
mutate(MATHS_bins =
cut(MATHS,
breaks = c(0,60,75,85,100))
)
ggbarstats(exam1,
x = MATHS_bins,
y = GENDER)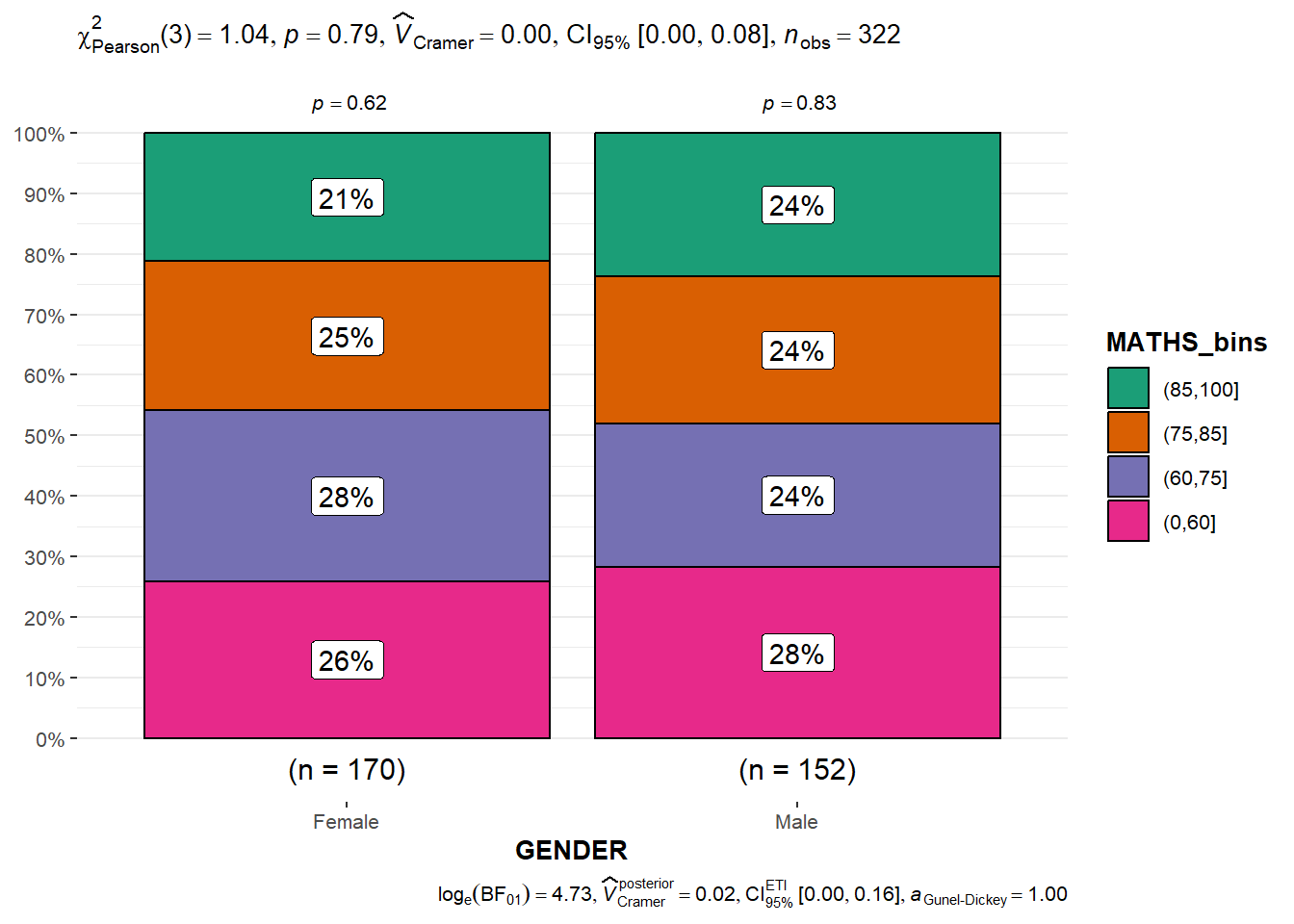
Visualising Uncertainty
Visualizing the uncertainty of point estimates: ggplot2 methods
Preparation
my_sum <- exam %>%
group_by(RACE) %>%
summarise(
n=n(),
mean=mean(MATHS),
sd=sd(MATHS)
) %>%
mutate(se=sd/sqrt(n-1))knitr::kable(head(my_sum), format = 'html')| RACE | n | mean | sd | se |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 193 | 76.50777 | 15.69040 | 1.132357 |
| Indian | 12 | 60.66667 | 23.35237 | 7.041005 |
| Malay | 108 | 57.44444 | 21.13478 | 2.043177 |
| Others | 9 | 69.66667 | 10.72381 | 3.791438 |
Plotting standard error bars of point estimates
ggplot(my_sum) +
geom_errorbar(
aes(x=RACE,
ymin=mean-se,
ymax=mean+se),
width=0.2,
colour="black",
alpha=0.9,
linewidth=0.5) +
geom_point(aes
(x=RACE,
y=mean),
stat="identity",
color="red",
size = 1.5,
alpha=1) +
ggtitle("Standard error of mean maths score by rac")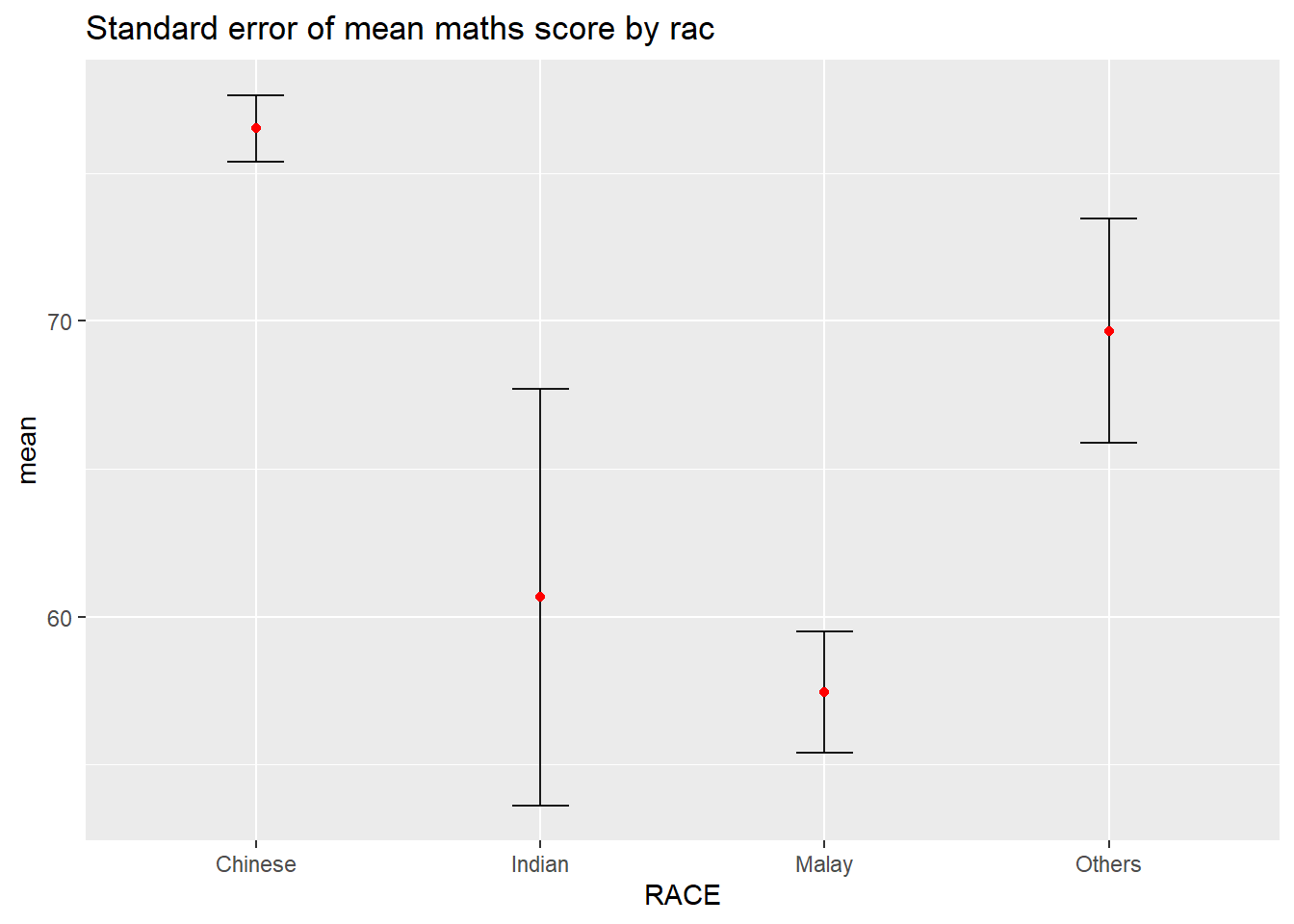
Plotting confidence interval of point estimates
ggplot(my_sum) +
geom_errorbar(
aes(x=reorder(RACE, -mean),
ymin=mean-1.96*se,
ymax=mean+1.96*se),
width=0.2,
colour="black",
alpha=0.9,
linewidth=0.5) +
geom_point(aes
(x=RACE,
y=mean),
stat="identity",
color="red",
size = 1.5,
alpha=1) +
labs(x = "Maths score",
title = "95% confidence interval of mean maths score by race")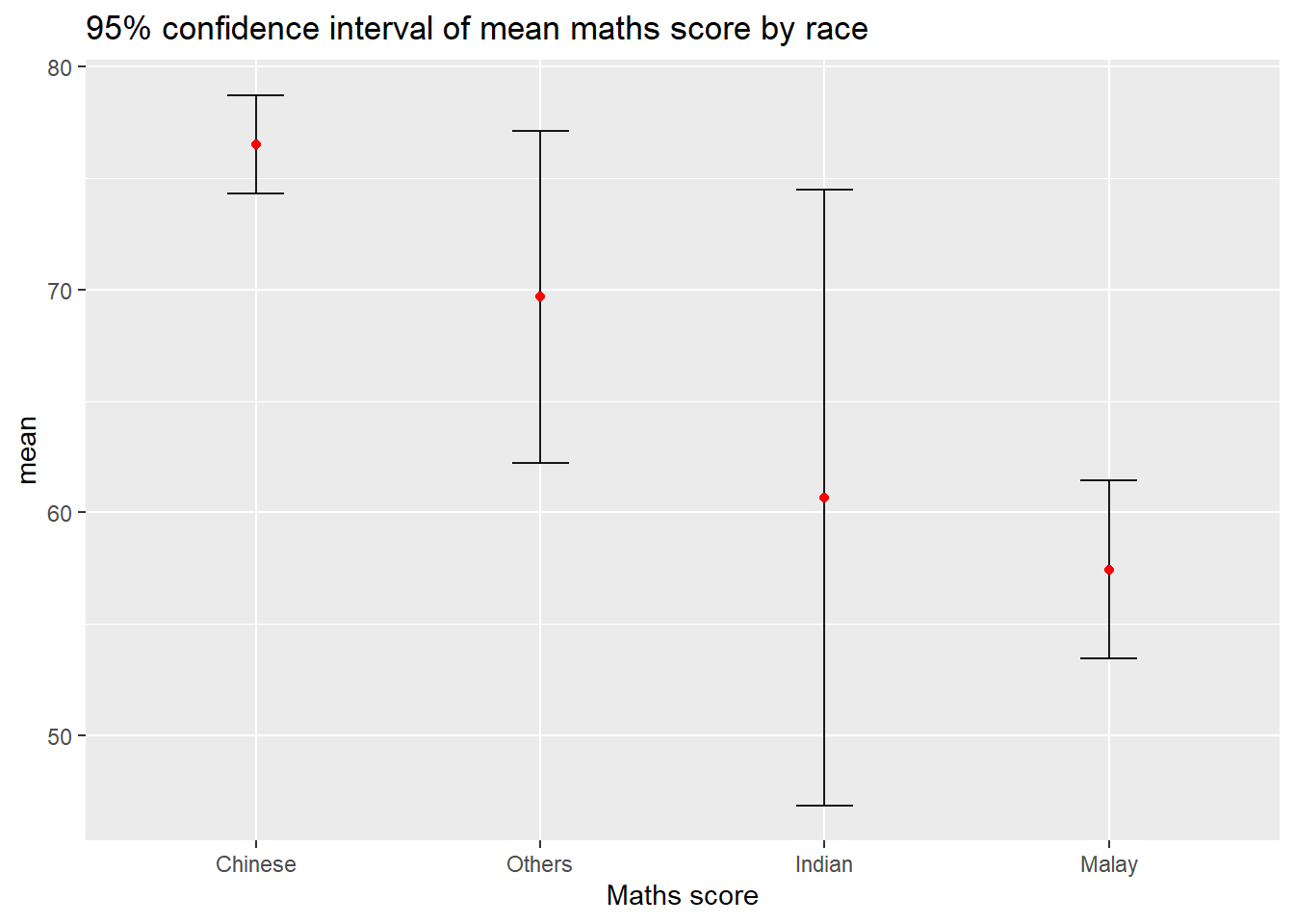
Visualizing the uncertainty of point estimates with interactive error bars
shared_df = SharedData$new(my_sum)
bscols(widths = c(5,7),
ggplotly(
ggplot(shared_df) +
geom_errorbar(aes(
x = reorder(RACE, -mean),
ymin = mean - 2.58 * se,
ymax = mean + 2.58 * se),
linewidth = 0.5, colour = "black", alpha = 0.9) +
geom_point(aes(
x = RACE,
y = mean,
text = paste("Race:", RACE,
"<br>N:", n,
"<br>Avg. Scores:", round(mean, 2),
"<br>99% CI:[", round((mean - 2.58 * se), 2), ",",
round((mean + 2.58 * se), 2), "]")),
stat = "identity",
color = "red", size = 1.5, alpha = 1) +
xlab("Race") +
ylab("Average Scores") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, vjust = 0.5, hjust = 1)) +
ggtitle("99% Confidence interval of average\nmaths scores by race"),
tooltip = "text"
),
DT::datatable(shared_df,
rownames = FALSE,
class = "compact",
width = "100%",
extensions = 'Buttons',
options = list(
dom = 'Blfrtip',
pageLength = 10,
scrollX = TRUE
),
colnames = c("No. of pupils", "Avg Scores", "Std Dev", "Std Error")) %>%
formatRound(columns = c('mean', 'sd', 'se'), digits = 2)
)Visualising Uncertainty: ggdist package
Visualizing the uncertainty of point estimates: ggdist methods
exam %>%
ggplot(aes(x = RACE,
y = MATHS)) +
stat_pointinterval() +
labs(
title = "Visualising confidence intervals of mean math score",
subtitle = "Mean Point + Multiple-interval plot")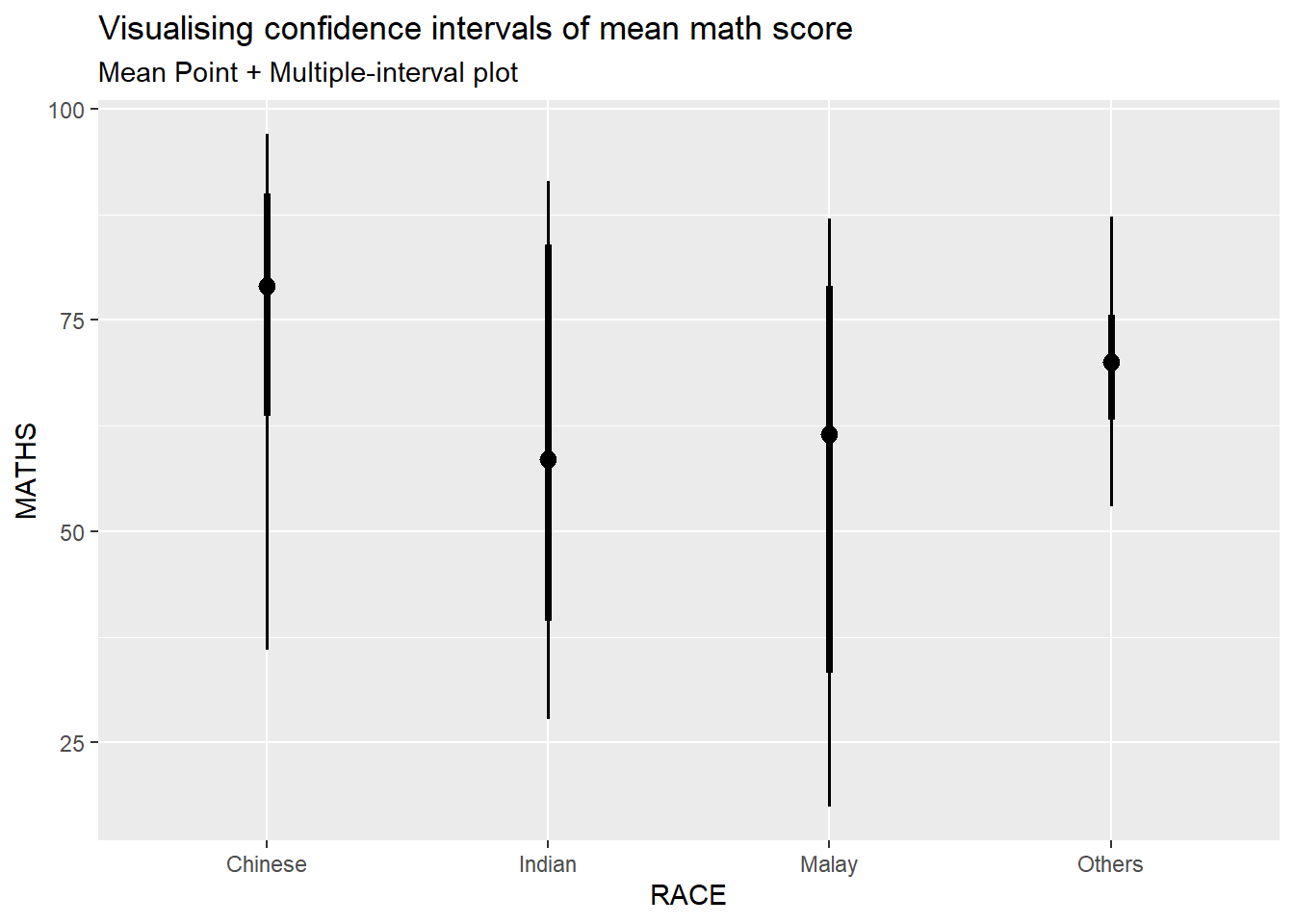
exam %>%
ggplot(aes(x = RACE, y = MATHS)) +
stat_pointinterval(.width = 0.95,
.point = median,
.interval = qi) +
labs(
title = "Visualising confidence intervals of median math score",
subtitle = "Median Point + Multiple-interval plot")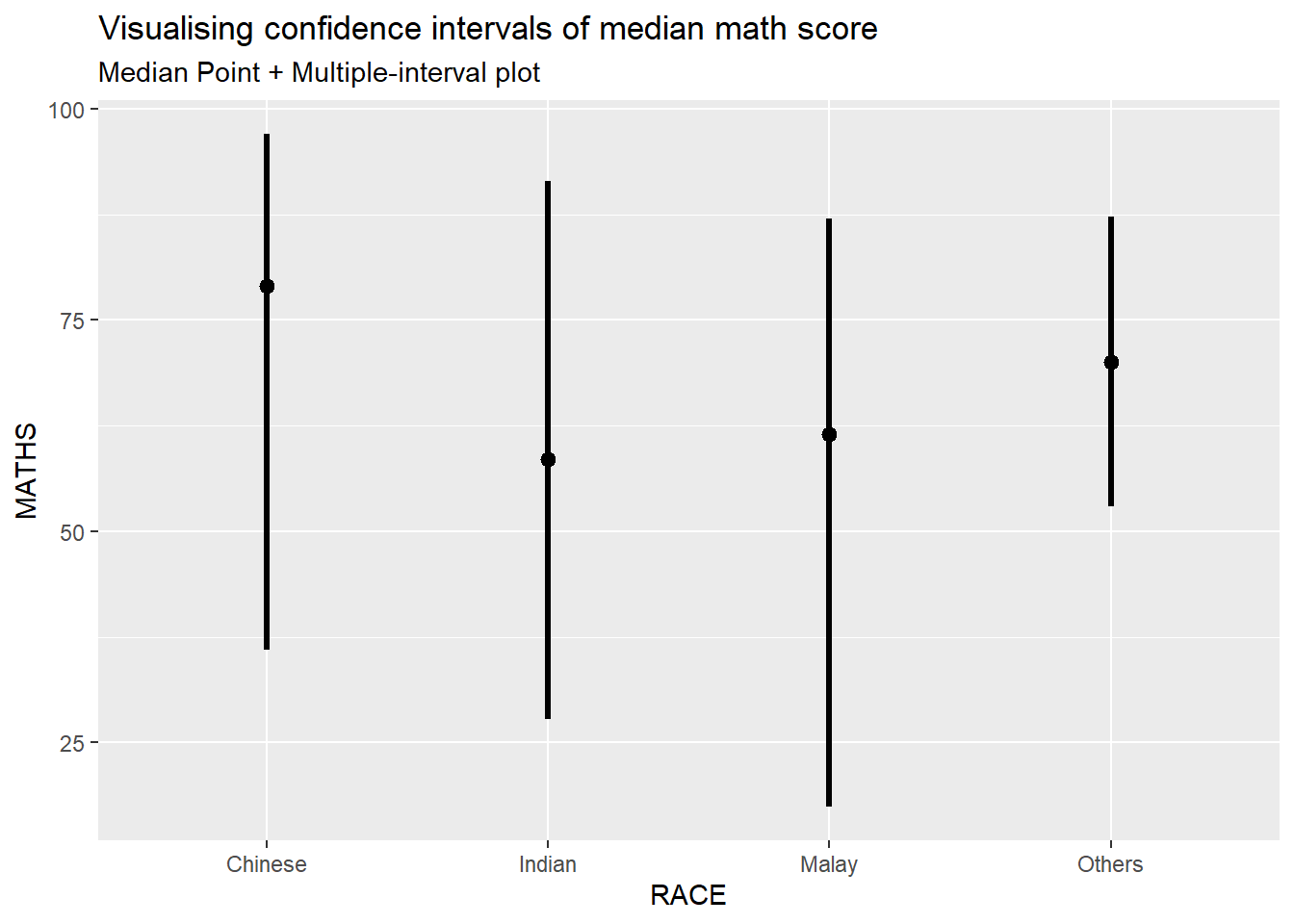
Visualizing the uncertainty of point estimates: ggdist methods
exam %>%
ggplot(aes(x = RACE,
y = MATHS)) +
stat_pointinterval(
show.legend = FALSE) +
labs(
title = "Visualising confidence intervals of mean math score",
subtitle = "Mean Point + Multiple-interval plot")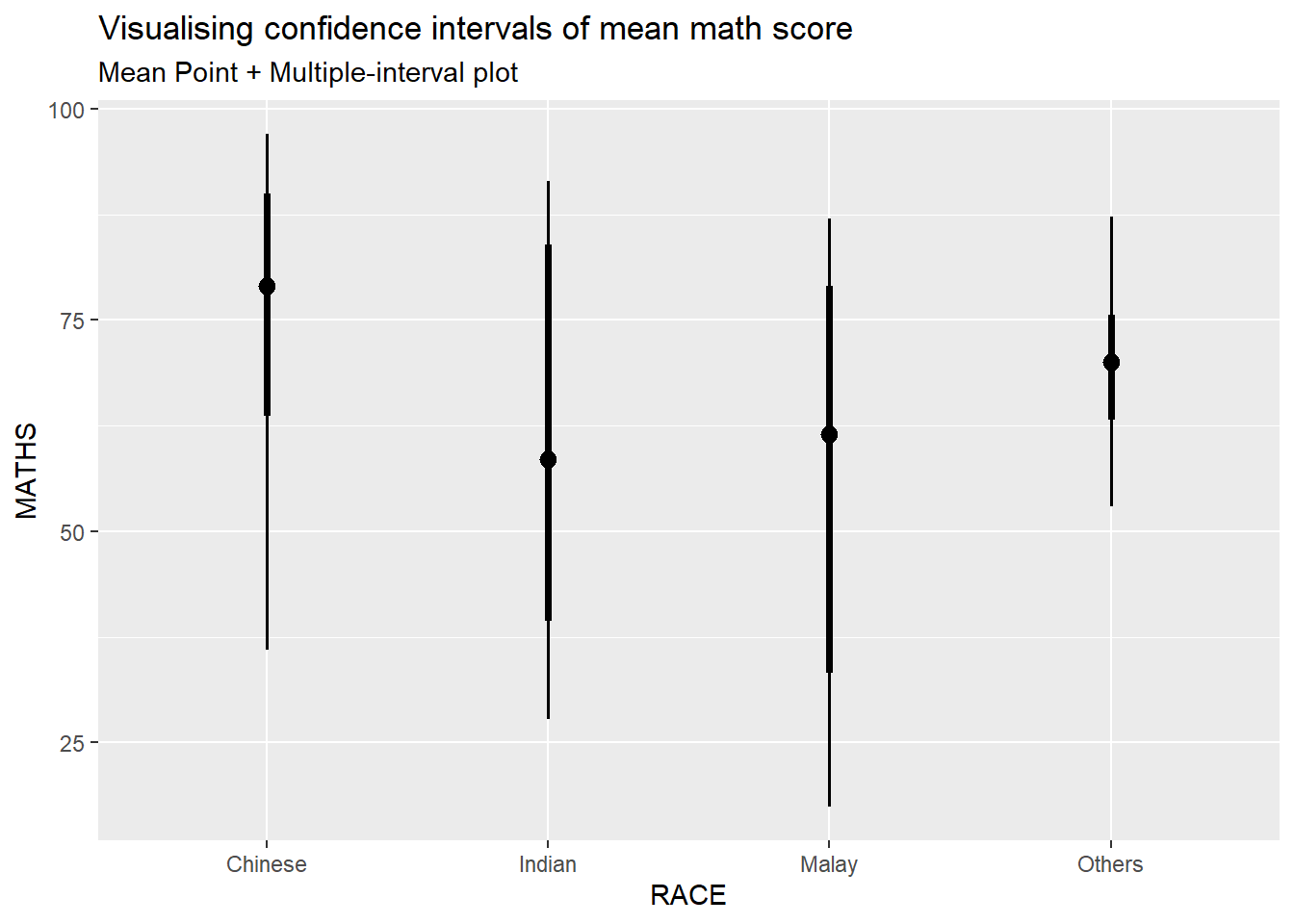
Visualizing the uncertainty of point estimates: ggdist methods
exam %>%
ggplot(aes(x = RACE,
y = MATHS)) +
stat_gradientinterval(
fill = "skyblue",
show.legend = TRUE
) +
labs(
title = "Visualising confidence intervals of mean math score",
subtitle = "Gradient + interval plot")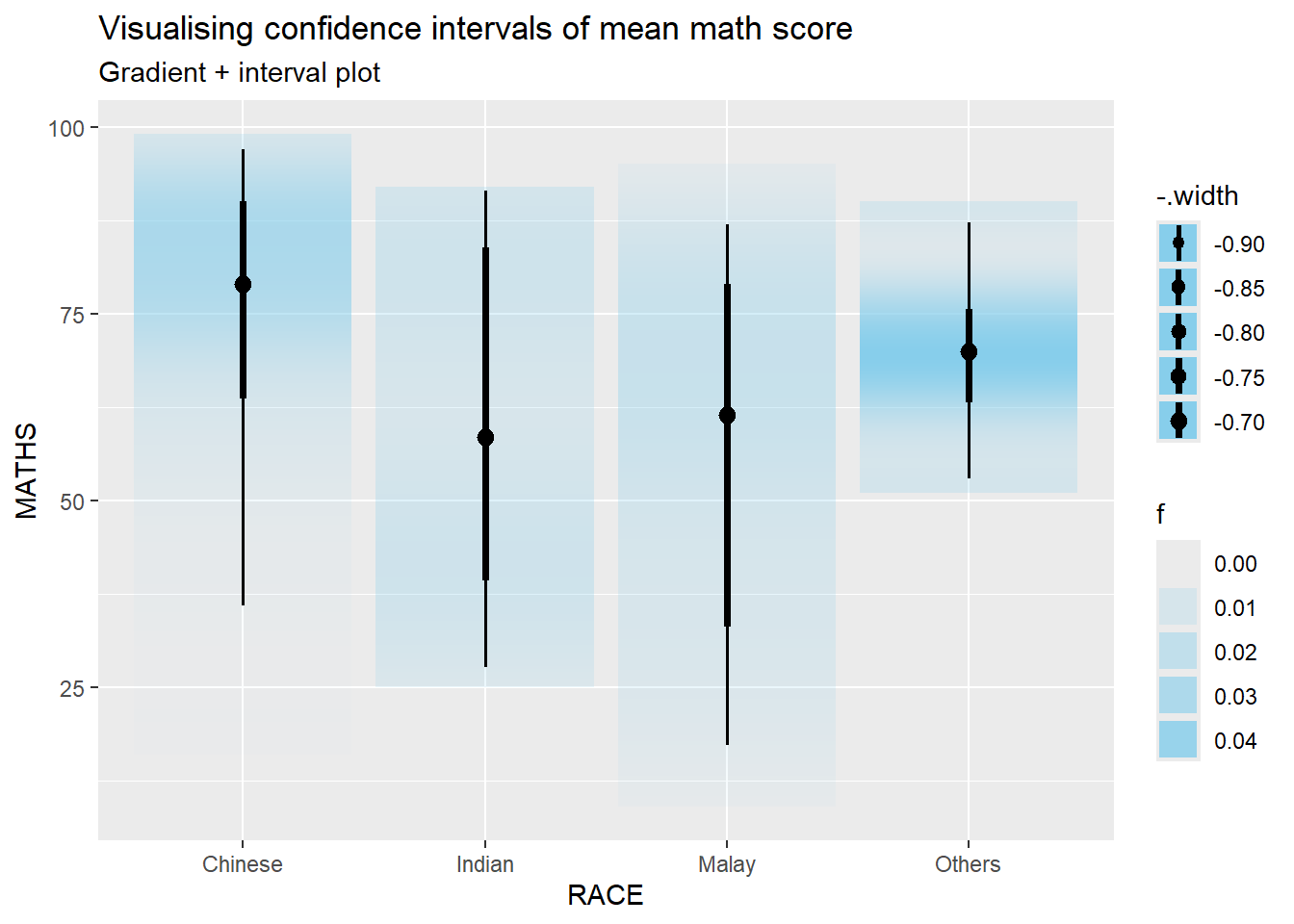
Visualising Uncertainty with Hypothetical Outcome Plots (HOPs)
Installing ungeviz package
devtools::install_github("wilkelab/ungeviz")library(ungeviz)ggplot(data = exam,
(aes(x = factor(RACE),
y = MATHS))) +
geom_point(position = position_jitter(
height = 0.3,
width = 0.05),
size = 0.4,
color = "#0072B2",
alpha = 1/2) +
geom_hpline(data = sampler(25,
group = RACE),
height = 0.6,
color = "#D55E00") +
theme_bw() +
transition_states(.draw, 1, 3)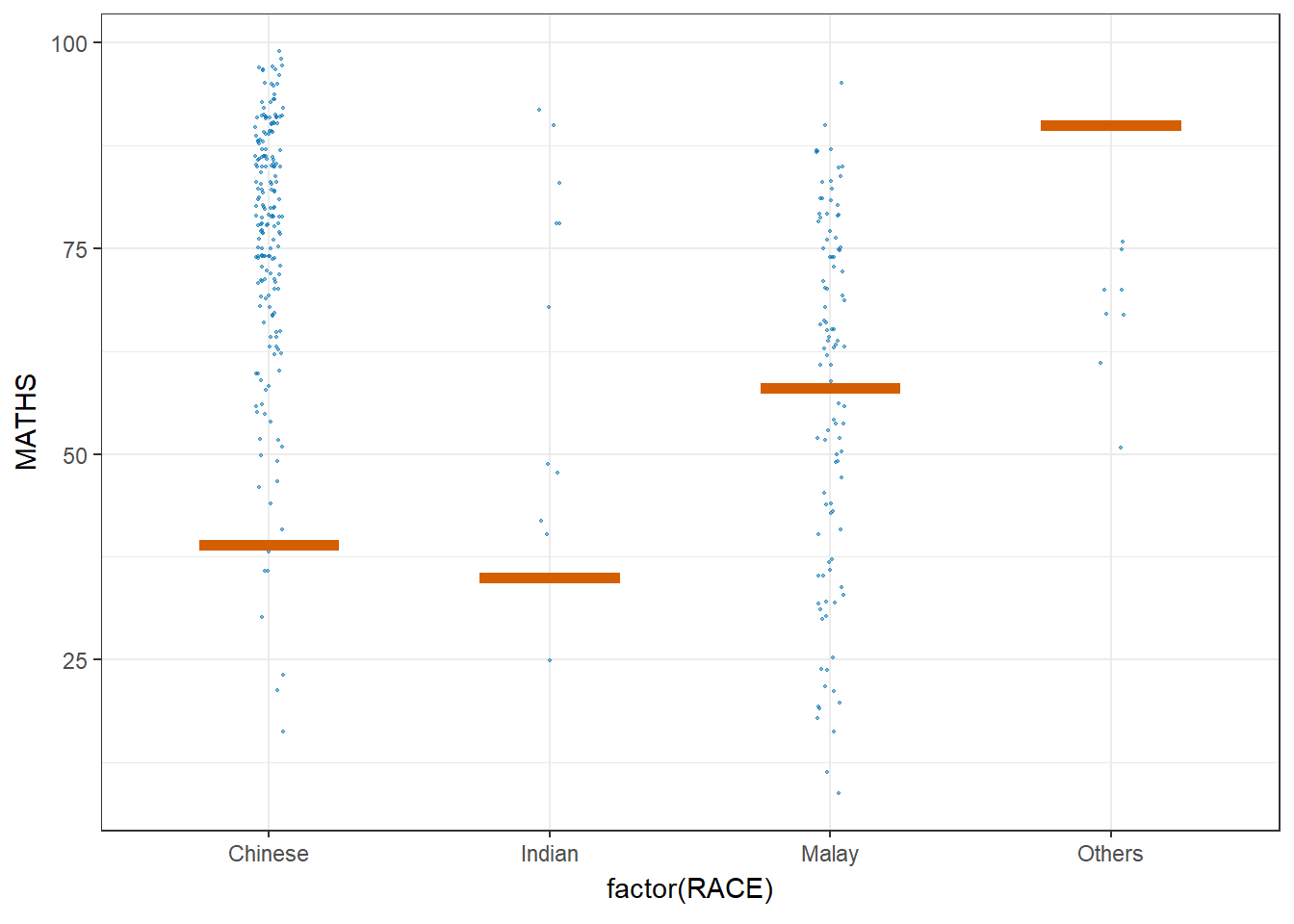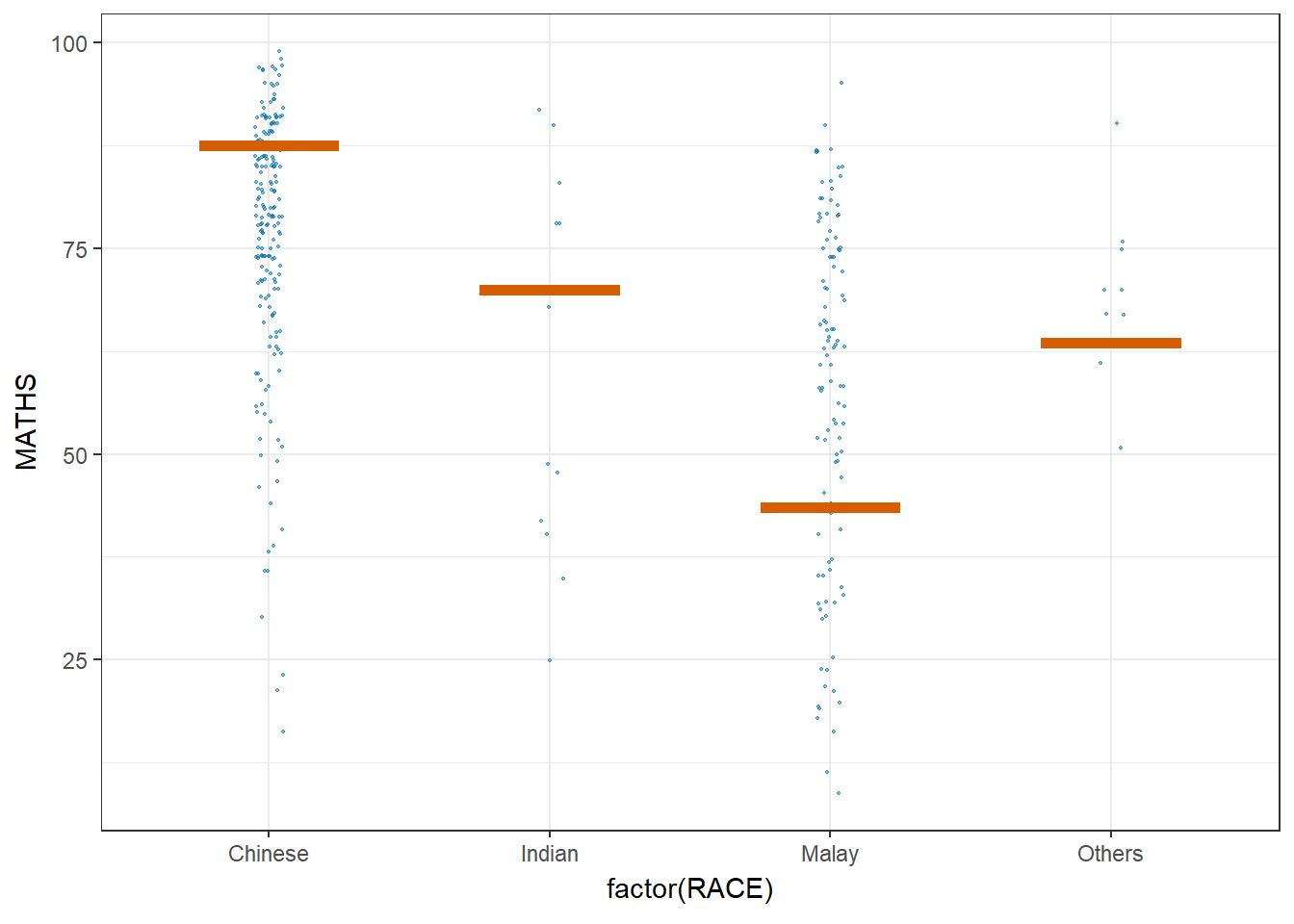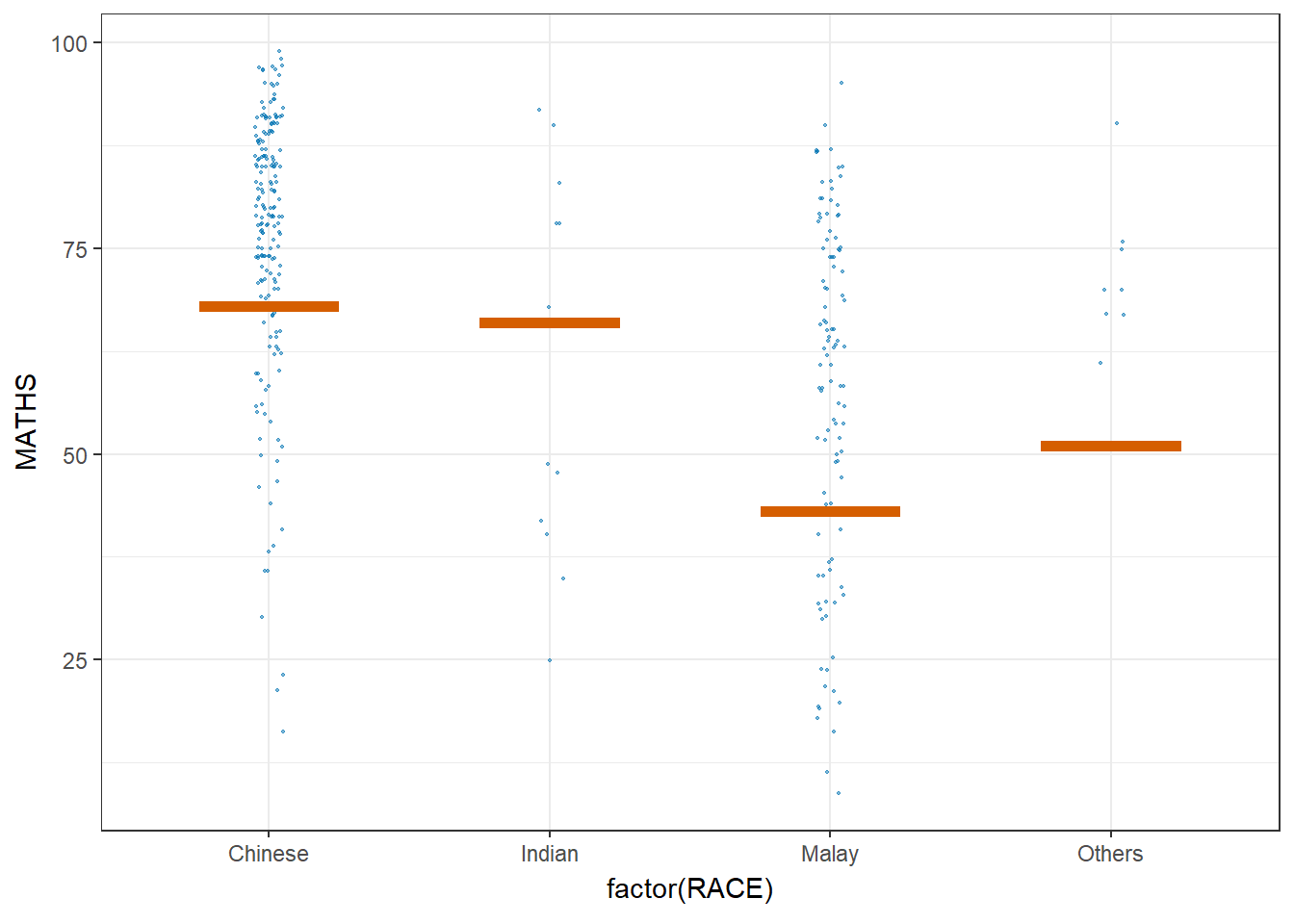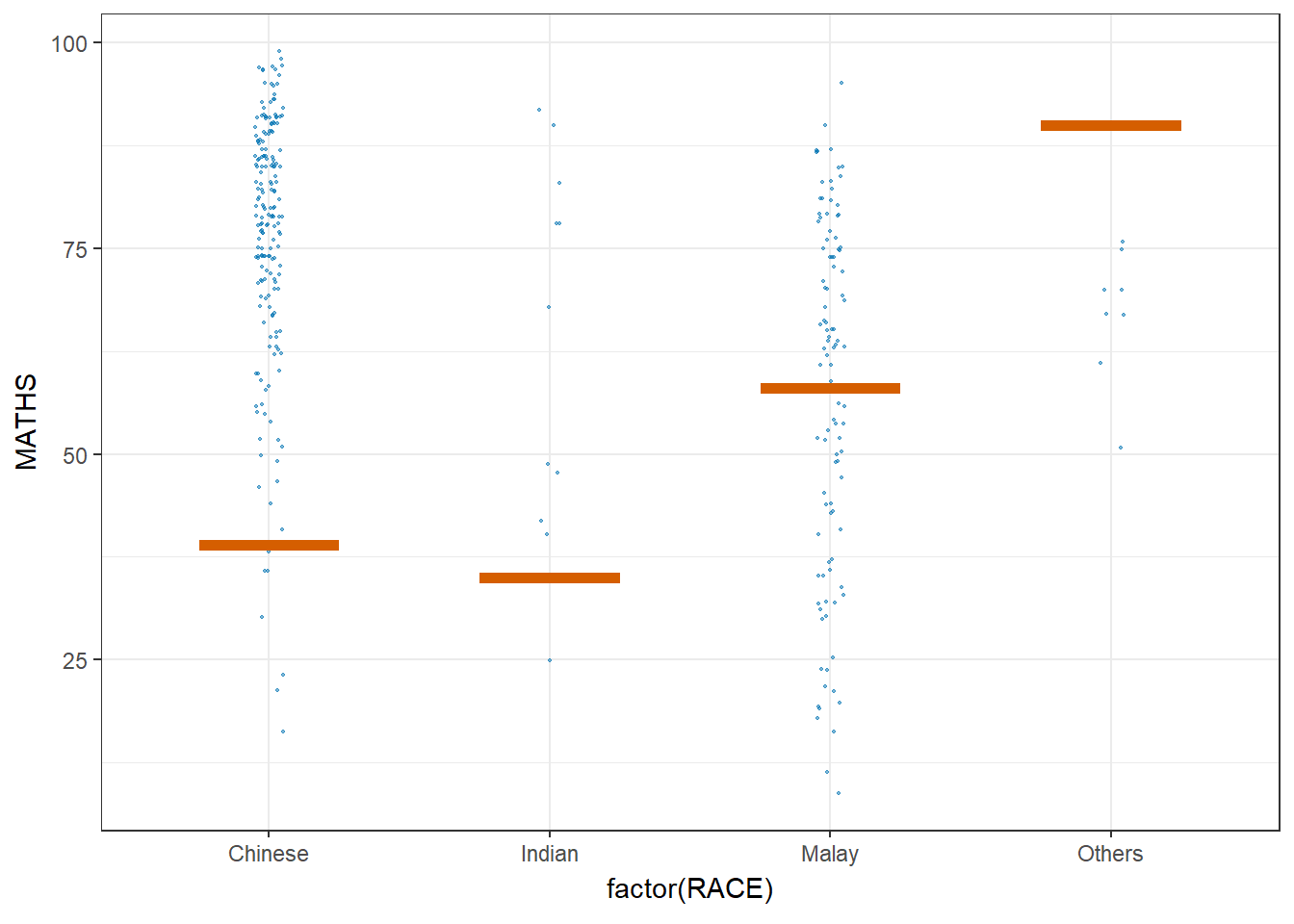
Funnel Plots for Fair Comparisons
FunnelPlotR methods
FunnelPlotR methods: The basic plot
funnel_plot(
.data = covid19,
numerator = Positive,
denominator = Death,
group = `Sub-district`
)
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 0 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. FunnelPlotR methods: Makeover 1
funnel_plot(
.data = covid19,
numerator = Death,
denominator = Positive,
group = `Sub-district`,
data_type = "PR", #<<
xrange = c(0, 6500), #<<
yrange = c(0, 0.05) #<<
)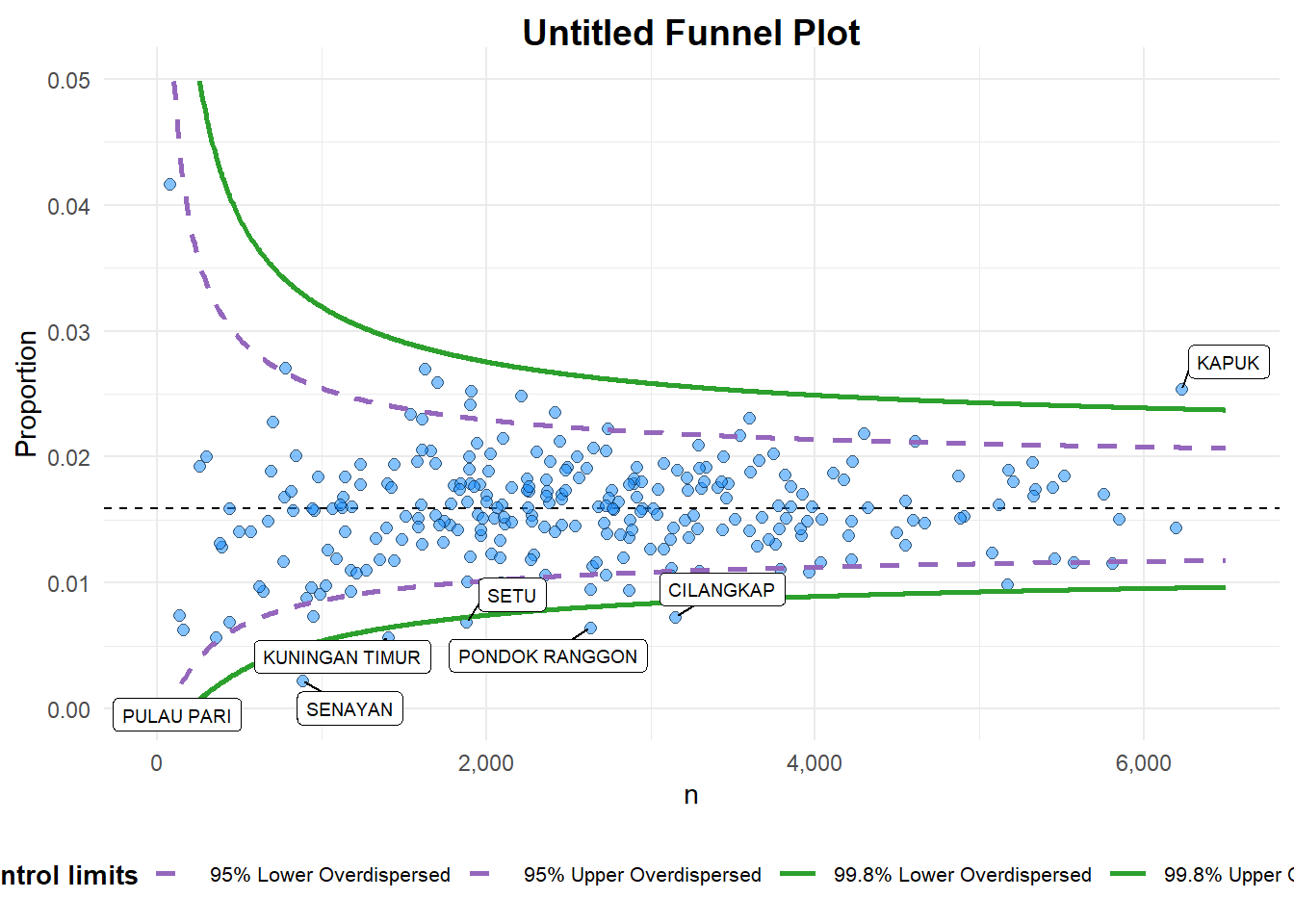
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 7 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. FunnelPlotR methods: Makeover 2
funnel_plot(
.data = covid19,
numerator = Death,
denominator = Positive,
group = `Sub-district`,
data_type = "PR",
xrange = c(0, 6500),
yrange = c(0, 0.05),
label = NA,
title = "Cumulative COVID-19 Fatality Rate by Cumulative Total Number of COVID-19 Positive Cases", #<<
x_label = "Cumulative COVID-19 Positive Cases", #<<
y_label = "Cumulative Fatality Rate" #<<
)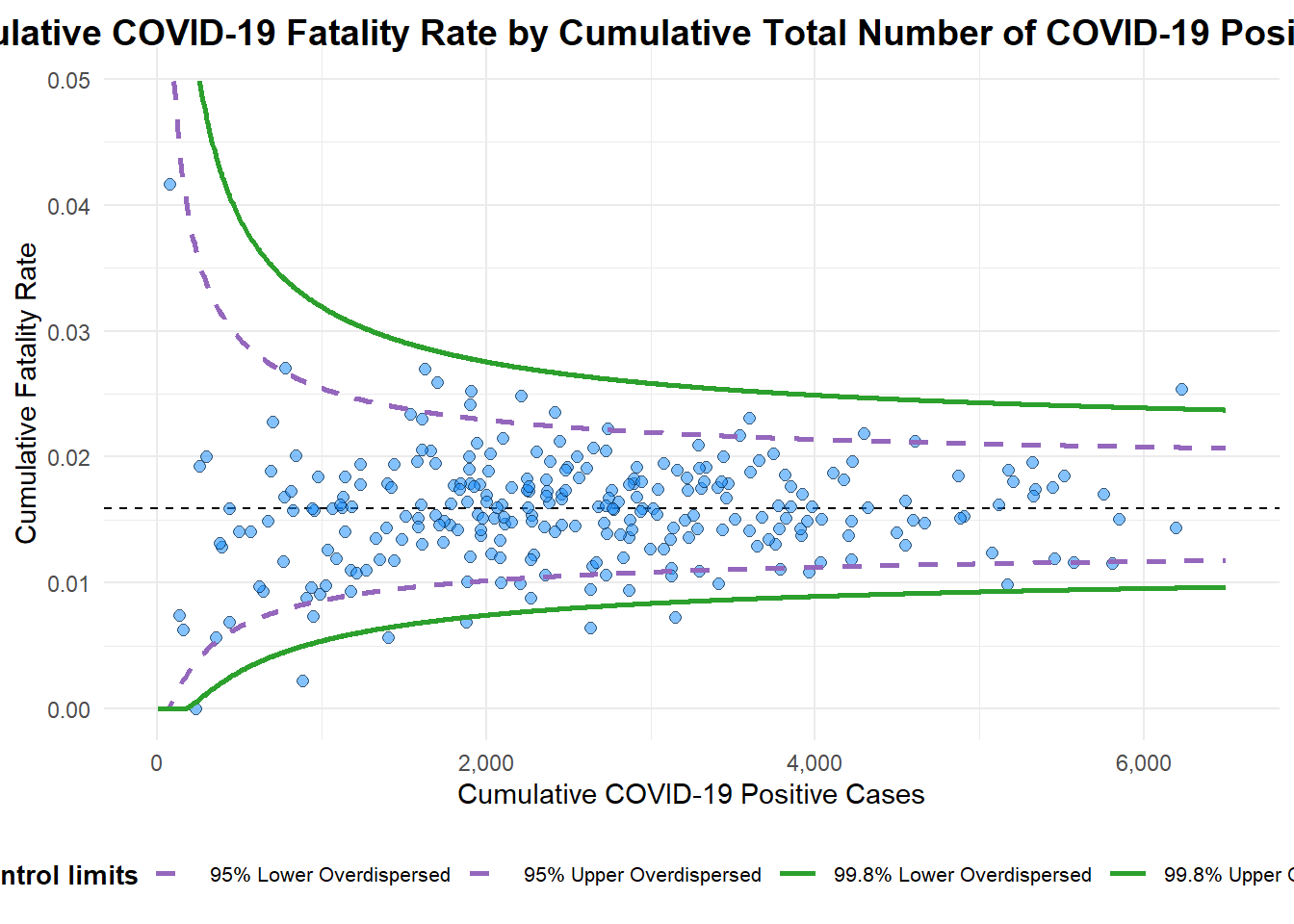
A funnel plot object with 267 points of which 7 are outliers.
Plot is adjusted for overdispersion. Funnel Plot for Fair Visual Comparison: ggplot2 methods
Computing the basic derived fields
df <- covid19 %>%
mutate(rate = Death / Positive) %>%
mutate(rate.se = sqrt((rate*(1-rate)) / (Positive))) %>%
filter(rate > 0)
fit.mean <- weighted.mean(df$rate, 1/df$rate.se^2)Calculate lower and upper limits for 95% and 99.9% CI
number.seq <- seq(1, max(df$Positive), 1)
number.ll95 <- fit.mean - 1.96 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ul95 <- fit.mean + 1.96 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ll999 <- fit.mean - 3.29 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
number.ul999 <- fit.mean + 3.29 * sqrt((fit.mean*(1-fit.mean)) / (number.seq))
dfCI <- data.frame(number.ll95, number.ul95, number.ll999,
number.ul999, number.seq, fit.mean)Plotting a static funnel plot
p <- ggplot(df, aes(x = Positive, y = rate)) +
geom_point(aes(label=`Sub-district`),
alpha=0.4) +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ll95),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40",
linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ul95),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40",
linetype = "dashed") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ll999),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
geom_line(data = dfCI,
aes(x = number.seq,
y = number.ul999),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
geom_hline(data = dfCI,
aes(yintercept = fit.mean),
size = 0.4,
colour = "grey40") +
coord_cartesian(ylim=c(0,0.05)) +
annotate("text", x = 1, y = -0.13, label = "95%", size = 3, colour = "grey40") +
annotate("text", x = 4.5, y = -0.18, label = "99%", size = 3, colour = "grey40") +
ggtitle("Cumulative Fatality Rate by Cumulative Number of COVID-19 Cases") +
xlab("Cumulative Number of COVID-19 Cases") +
ylab("Cumulative Fatality Rate") +
theme_light() +
theme(plot.title = element_text(size=12),
legend.position = c(0.91,0.85),
legend.title = element_text(size=7),
legend.text = element_text(size=7),
legend.background = element_rect(colour = "grey60", linetype = "dotted"),
legend.key.height = unit(0.3, "cm"))
p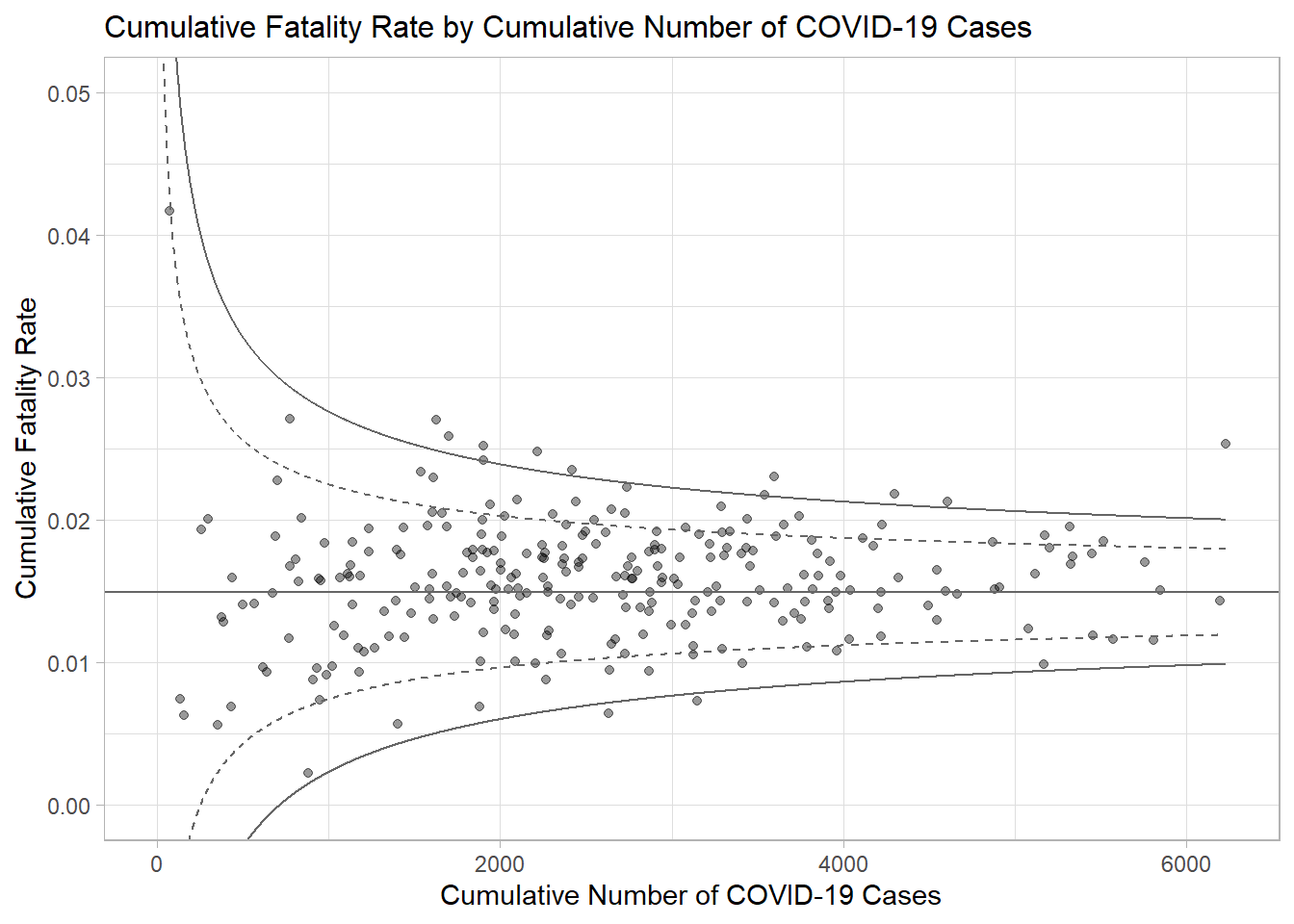
Interactive Funnel Plot: plotly + ggplot2
fp_ggplotly <- ggplotly(p,
tooltip = c("label",
"x",
"y"))
fp_ggplotly